One to One and Many to One Mapping in Hibernate by R4R Team
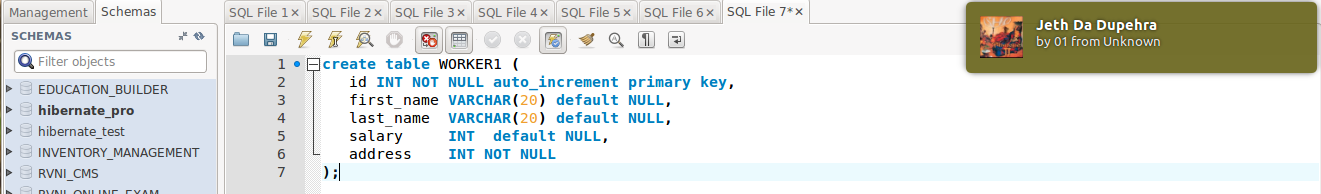
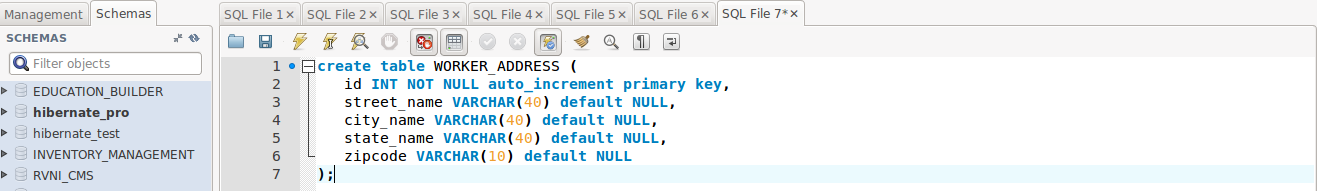


|
@Entity Annotation: |
The EJB 3 annotations standard Step 1: In the first step we have to import javax.persistence Step 2: When we used the @Entity annotation to the HibernateMapping class it marked class to as an entity bean, so it must have a no-argument constructor that is visible with at least protected scope. |
|
@Table Annotation: |
@Table annotation allows to specify the details of the table that will be used to persist the entity in the database. @Table annotation provides four attributes allowing override the name of the table, its catalogue, and its schema, and enforce unique constraints on columns in the table. |
|
@Id and @GeneratedValue Annotations: |
Each entity bean always will have a primary key, which annotated on the class with the @Id annotation. The primary key can be a single field or a combination of multiple fields depending on table structure. By default, @Id annotation will automatically determine the most appropriate primary key generation strategy to be used but can override this by applying the @GeneratedValue annotation which takes two parameters strategy and generator, that is default key generation strategy. |
|
@Column Annotation: |
element maps the unique ID attribute in class to the primary key of the database table. Attribute name of the id element refers to the property in the class and the column attribute refers to the column in the database table. Attribute type holds the hibernate mapping type, this mapping types will convert from Java to SQL data type.@Column annotation is used to specify the details of the column to which a field or property will be mapped. You can use column annotation with the following most commonly used attributes: Some common attribute are given below: Name attribute permits the name of the column to be explicitly specified. Length attribute permits the size of the column used to map a value articularly for a String value. Nullable attribute permits the column to be marked NOT NULL when the schema is generated. Uniqueattribute permits the column to be marked as containing only unique values. |
Leave a Comment:
Search
Categories
- Introduction of Mapping in Hibernate with Example
- Types of Mapping in Hibernate or Relationship Multiplicity
- One to One and Many to One Mapping in Hibernate
- One to Many Mapping in Hibernate
- Many to Many in Hibernate
- Collection Mapping and Component Mapping Hibernate
- Introduction of Mapping in Hibernate with Example
- Types of Mapping in Hibernate or Relationship Multiplicity
- One to One and Many to One Mapping in Hibernate
- One to Many Mapping in Hibernate
- Many to Many in Hibernate
- Collection Mapping and Component Mapping Hibernate
- Hibernate Tutorial for beginners with Examples
- Mapping in Hibernate or Association Mapping in Hibernate
- Database Portability Considerations
- Mapping with Annotation in Hibernate
- Collection mapping
- Basic O/R Mapping
- Hibernate Mapping types
- Caching machanism
- HQL: The Hibernate Query Language
- Join in hibenrate
- Advanced collection mappings
- Batch processing
- Native SQL
- Criteria Queries
- Fetching strategies in Hibernate From the DataBase
- Hibernate Step By Step Application Using Struts On NetBeans
- Hibernate Step By Step Application Using Swing On NetBeans
- Hibernate Step By Step Application Using Spring On NetBeans
- Hibernate Step By Step Application Using Servlet On NetBeans
- Interceptors and events
- Filtering data in Hibernate
- Working with objects
- XML Mapping in Hibernate
- Transactions and Concurrency in Hibernate
- Inheritance mapping
- Component Mapping In Hibernate
- Use of Configuration in Hibernate
- Persistent Classes in Hibernate
- Toolset Guide in Hibernate
- Difference Between Save and Persist Method
- Core Java
- Core Java Interview Question Answers
- Hibernate
- Hibernate Interview Question Answers
- Servlet
- Servlet Interview Question Answers
- MYSQL
- MYSQL Interview Question Answers
- JavaServer Pages (JSP)
- JavaServer Pages (JSP) Interview Question Answers
- Spring
- Spring Interview Question Answers
- Struts 2
- Struts 2 Interview Question Answers
- J2ME
- J2ME Interview Question Answers
- General Knowledge
- General Knowledge Interview Question Answers
- Spring boot
- Spring boot Interview Question Answers
- Python
- Python Interview Question Answers
- c language
- c language Interview Question Answers
- C++ language
- C++ language Interview Question Answers
- Data Structure using c
- Data Structure using c Interview Question Answers